Microsoft buys stake in London Stock Exchange Group in twist on digital transformation deals

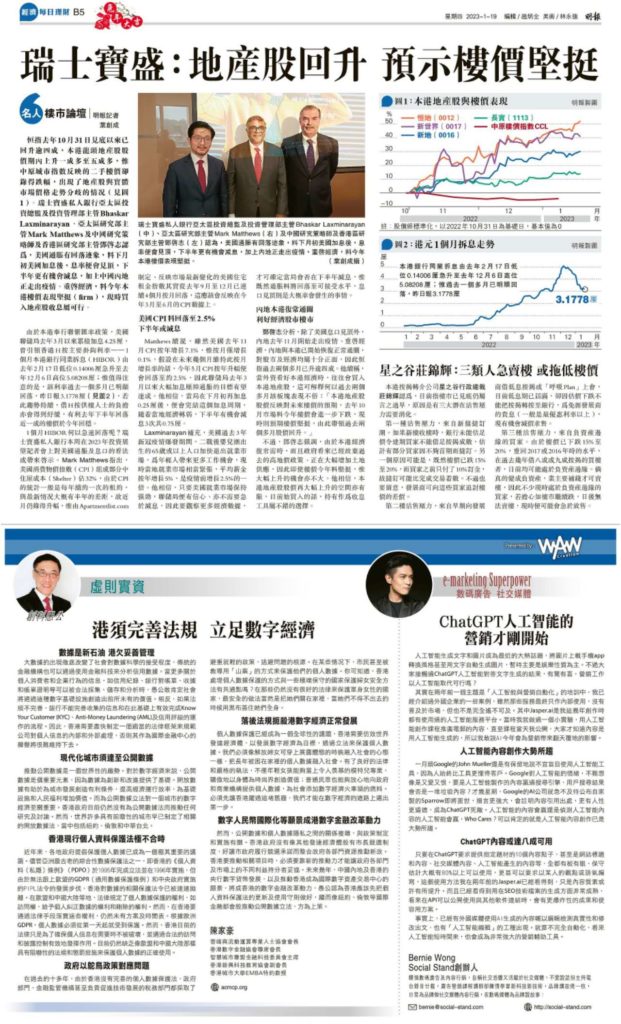
Microsoft has announced a 10-year strategic partnership with the London Stock Exchange Group (LSEG) to put the financial markets providers’ infrastructure and data analytics onto the Microsoft cloud – and has acquired a 4% stake in the group in the process.
Seasoned cloud industry watchers will know how these sorts of strategic partnerships play out. The client comes on board for an undisclosed amount, the right noises are made around improving customer and end-user experience and productivity, and the vendor takes a seat on board. This, however, is different. Microsoft has agreed to purchase an approximately 4% equity stake in LSEG through the acquisition of shares from the Blackstone/Thomson Reuters Consortium.
Microsoft noted that with LSEG’s acquisition of data services provider Refinitiv, completed at the beginning of 2021, the company had its own impressive technological stack in terms of infrastructure and data. LSEG has ‘differentiated itself in the market with an end-to-end proposition across trading, execution, data and analytics solutions,’ Microsoft noted.
Firms across capital markets are facing an ‘increasingly complex operating environment’, Microsoft added, with traditional streams of revenue becoming ‘more challenging.’ A tech stack underpinned by cloud and AI technologies is therefore necessary to break down the old, siloed platforms and deliver the best client experience, insights and tools. “LSEG has already started to address these issues for their customers, and through this strategic partnership, we will accelerate that transformation,” Microsoft added.
In terms of nuts and bolts, LSEG will utilise a wide part of the Microsoft enterprise collaboration suite. LSEG’s technology infrastructure and data and analytics platforms – including Refinitiv platforms – will be migrated onto the Microsoft cloud. The companies promised an open financial data platform which will ‘enable seamless data democratisation, collaboration and new monetisation opportunities across the financial services ecosystem.’ Internal collaboration will come through a bespoke LSEG Workspace on Microsoft Teams offering, while enhanced Excel integration was also noted.
David Schwimmer, the CEO of the London Stock Exchange Group – no, not that one – said: “Bringing together our leading data sets, analytics and global customer base with Microsoft’s comprehensive and trusted cloud services and global reach creates attractive revenue growth opportunities for both companies.”
Among Microsoft’s other customer and partnership wins in the most recent quarter include Informatica, which has become an initial partner of Microsoft’s Intelligent Data Platform partner ecosystem, and Our Future Health, pitched as the UK’s largest-ever health research programme.
Source from: CloudTech